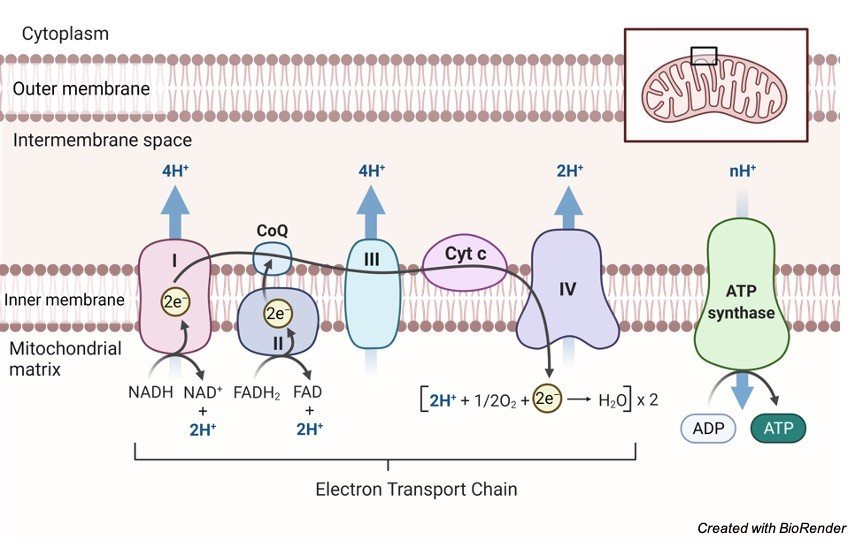
Furthermore 3D tomography of. D the intermembrane space to the matrix.

Solved 1 22 The Chemiosmotic Process In Chloroplasts Involves The A Establishment Of A Proton Gradient Across The Thylakoid Membrane B Diffusion Of Electrons Through The Thylakoid Membrane C Reduction Of Water To
In oxidative phosphorylation the hydrogen ion gradient formed by the electron transport chain is used by ATP synthase to form ATP.

. The turning of this molecular machine harnesses the potential energy stored in the hydrogen ion gradient to add a phosphate to ADP forming ATP. Chemiosmosis in chloroplast involves which of the following processes. Chemiosmosis is the movement of ions across a semipermeable membrane bound structure.
Chemiosmosis involves the pumping of protons through special channels in the membranes of mitochondria from the inner to the outer compartment. The pumping establishes a proton H gradient. Formation of glucose using.
The chemiosmotic theory states that molecules like glucose are metabolised to produce acetyl CoA in the form of an energy-rich intermediate whereas Photosynthesis is the process through which a plant converts light energy into chemical energy to create food. Reduction of water to produce ATP C. Chemiosmosis involves the pumping of protons through special channels in the membranes of mitochondria from the inner to the outer compartment.
Chemiosmosis is the process through which cells produce ATP for energy in the cellular respiration process. Chemiosmosis in the organelles takes place during light-dependent reactions of photosynthesis when the energy of photoexcited electrons is used to make ATP for dark reactions. 24 What does the chemiosmotic process in chloroplasts involve.
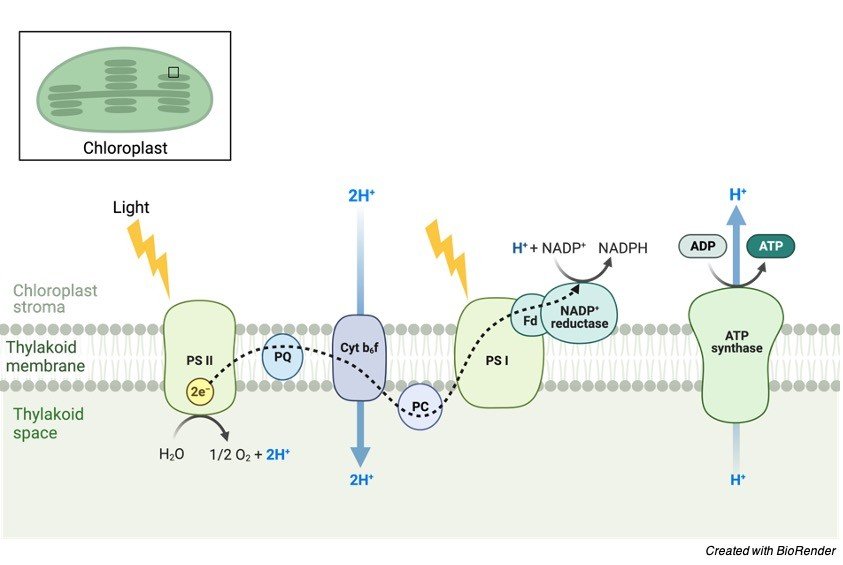
This process occurs within the chloroplasts on the thylakoid membranes that are stacked into structures called grana. Also it is the movement of ions across semipermeable membrane down their electrochemical gradients. C the stroma to the thylakoid space.
After the gradient is established protons diffuse down the gradient through a transport protein called ATP synthase. The chemiosmotic process in chloroplasts involves the _____. The outside P side is the bacterial periplasmic space mitochondrial intermembrane space or chloroplast lumen.
Chemiosmosis in Chloroplasts Chloroplasts are the organelles present in photosynthetic autotrophs. Establishment of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane D. This process also involves an electron transport chain proton gradient and chemiosmosis of H but it takes place across the inner membrane of the bacterium or archaeon since they have no mitochondria.
This process is related to osmosis. In living organisms the process of converting nutrients into useable energy is called cellular respiration. B the matrixto the stroma.
We will study their meanings and processes in detail. The movement of hydrogen atoms across a. The movement of hydrogen ions across a.
A estalishments of a proton gradient across the thylakoid membrane B diffusion of electrons through the thylakoid membrane C reduction of water to produce oxygen D formation of glucose from carbon dioxide D thylakoid membranes and inner mitochondrial membranes. Chemiosmosis - ATP Synthesis in Chloroplasts Photosynthesis is a process that takes place in the leaves of plants where carbon dioxide and water is converted to carbohydrates also producing oxygen. It generates energy in the same way as a water wheel generates power.
In chloroplast chemiosmotic coupling is an important factor in ATP production through proton gradient establishment. This is where chemiosmosis comes into play and in cells that rely on respiration this. E the thylakoid space to the stroma.
Diffusion of electrons through the thylakoid membrane B. A establishment of a proton gradient B diffusion of electrons through the thylakoid membrane C reduction of water to produce ATP energy D movement of water by osmosis into the thylakoid space from the stroma E formation of glucose using carbon dioxide NADPH and ATP Answer. Is the bacterial cytoplasm mitochondrial matrix or chloroplast stroma.
After the gradient is established protons diffuse down the gradient through a transport protein called ATP synthase. Chemiosmosis is the process that allows the diffusion of a molecule or an atom through the membrane. Involve electron transport chains which excite electrons and produce energy this energy is used to pump protons H ions across a membrane against the concentration gradient as the protons passively diffuse back across the membrane they come in through ATP synthase and ATP is produced this part is called oxidative phosphorylation Differences.
In mitochondria chemiosmosis translocates protons fromthe matrix into the intermembrane space whereas in chloroplasts chemiosmosis translocates protons from A the stroma to the photosystemII. The movement of glucose through the cell. The movement of electrons across the cell.
Plants produce ATP during photosynthesis in the chloroplast in addition to the ATP they generate through cellular respiration in mitochondria. Let us first understand the structure of chloroplasts. The pumping establishes a proton H gradient.
Chemiosmosis Definition Mechanism And Function

Solved 22 The Chemiosmotic Process In Chloroplasts Involves Chegg Com
0 Comments